How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to intricate drone racing. Mastering drone operation requires understanding its mechanics, adhering to safety protocols, and developing skillful piloting techniques. This guide provides a structured approach, covering everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers and legal considerations, empowering you to confidently take to the skies.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource to help you understand this is available at how to operate a drone. This will provide you with the knowledge needed to confidently and safely operate your drone, ensuring both your safety and the safety of those around you.
We will explore the essential components of a drone, detailing their functions and troubleshooting common issues. We’ll then guide you through pre-flight procedures, basic flight controls, and advanced techniques like waypoint navigation. Crucially, we’ll address safety regulations and maintenance, ensuring responsible and enjoyable drone operation. Prepare for takeoff!
Drone Parts and Components
Understanding the individual components of a drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section details the key parts, their functions, common problems, and troubleshooting tips. Different drone types also utilize varying component configurations, which will be explored.
Drone Component Overview
The following table summarizes the major components of a typical drone, their functions, common issues, and troubleshooting steps.
| Component | Function | Common Issues | Troubleshooting Tips |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Generate thrust for flight and maneuverability. | Bent or damaged propellers, imbalance. | Inspect for damage and replace if necessary. Balance propellers using a balancing tool. |
| Motors | Rotate the propellers, providing the drone’s power. | Motor failure, overheating, inconsistent speed. | Check motor connections, ensure proper cooling, replace faulty motors. |
| Flight Controller | The “brain” of the drone, controlling all flight functions. | Software glitches, sensor malfunctions, connection problems. | Check firmware updates, recalibrate sensors, inspect connections. |
| Battery | Powers the drone’s motors and electronics. | Low battery life, swelling, damage. | Charge fully, avoid overcharging, replace damaged batteries. |
| GPS Module (if equipped) | Provides location data for autonomous flight and stability. | Weak signal, inaccurate location data. | Ensure clear sky view, check GPS settings. |
| Camera (if equipped) | Captures images and videos. | Lens smudges, poor image quality. | Clean the lens, adjust camera settings. |
| Remote Controller | Used to control the drone’s flight and camera functions. | Low battery, connection issues. | Charge the controller, check controller and drone connections. |
Drone Types and Component Variations
While quadcopters (four rotors) are the most common, other configurations exist. Hexacopter (six rotors) offer increased redundancy and stability, while octocopters (eight rotors) provide even greater stability and payload capacity. The number of motors, propellers, and the flight controller’s complexity scale accordingly.
Drone Battery Specifications and Charging
Drone batteries typically use Lithium Polymer (LiPo) technology. A typical battery might have a voltage of 11.1V (3S) or 14.8V (4S), with capacities ranging from 1500mAh to 5000mAh or more. Always charge LiPo batteries using a suitable LiPo charger that monitors voltage and current to prevent damage or fire. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully for charging procedures and safety precautions.
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist is essential to ensure safe and reliable operation. This includes checking the drone’s physical condition, calibrating sensors, and verifying connectivity.
Pre-Flight Checklist
- Inspect propellers for damage.
- Check battery level and charge if necessary.
- Verify all connections are secure.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Check GPS signal strength (if applicable).
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Establish a stable connection between the drone and controller.
- Review the surrounding environment for hazards.
Compass and Sensor Calibration
Calibrating the compass and IMU is crucial for accurate flight and stability. Failure to calibrate can lead to erratic behavior and potential crashes. Most drones have built-in calibration procedures within their settings menu. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper calibration techniques.
Powering On and Connecting
The power-on sequence typically involves first turning on the drone’s battery, then the remote controller. The drone should automatically connect to the controller if the binding process has been completed correctly. Check the drone’s display or the controller’s screen for connection status.
Basic Flight Controls
Understanding the basic flight controls is fundamental to safe and successful drone operation. This section details the functions of the control sticks and Artikels the procedures for takeoff, hovering, and landing.
Remote Controller Functions
Standard drone controllers typically have two joysticks. The left stick generally controls the drone’s altitude and direction, while the right stick controls yaw (rotation) and pitch/roll (tilting).
Takeoff, Hovering, and Landing Procedures
These maneuvers are the foundation of drone piloting. Proper technique is essential for safety and control.
- Takeoff:
- Ensure a clear and open space.
- Slowly increase throttle (left stick upwards).
- Maintain a stable hover once airborne.
- Hovering:
- Maintain a steady throttle level.
- Use small, precise movements of the control sticks to adjust position.
- Landing:
- Slowly lower the throttle (left stick downwards).
- Maintain control until the drone gently touches down.
Flight Modes
Many drones offer various flight modes to cater to different skill levels and situations. Beginner mode often limits speed and responsiveness, while attitude mode provides more control over the drone’s orientation. GPS mode uses satellite data for position holding and autonomous flight features.
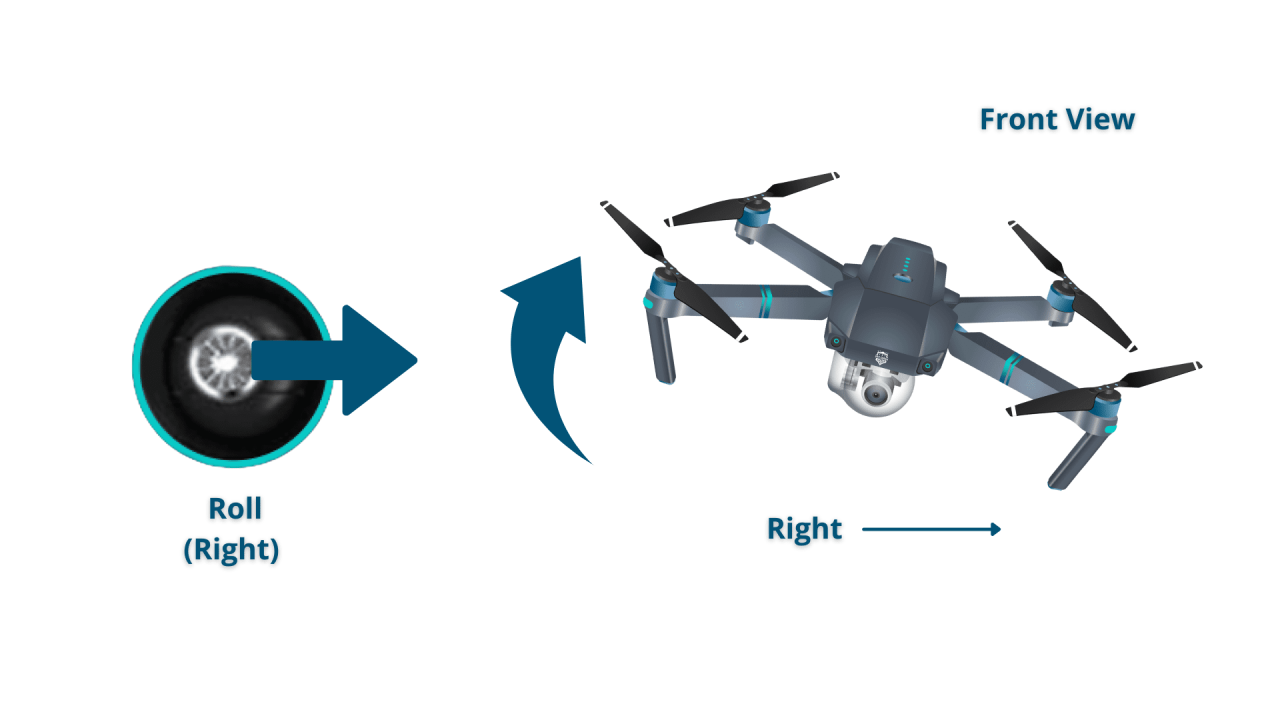
Advanced Flight Techniques
Once comfortable with basic flight, you can explore more advanced maneuvers. These require practice and a good understanding of drone dynamics. Safety is paramount when attempting these techniques.
Advanced Maneuvers
| Maneuver | Description | Control Inputs | Safety Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Turns | Rotating the drone around its vertical axis. | Right stick left/right. | Maintain sufficient altitude and awareness of surroundings. |
| Flips | Rapidly rotating the drone 360 degrees around an axis. | Specific button combinations on the controller (varies by drone). | Ensure ample space and avoid obstacles. |
| Rolls | Rotating the drone around its longitudinal axis. | Combination of stick movements (varies by drone). | Maintain altitude and be aware of surroundings. |
GPS-Assisted Flight
GPS features enable autonomous flight and waypoint navigation. This allows you to plan a flight path and have the drone follow it automatically. This is helpful for tasks like aerial photography or inspections.
Flight Planning with Drone Software
Dedicated drone software allows for detailed flight planning. You can define waypoints, altitudes, and camera settings to create a precise flight plan. The software typically connects to the drone wirelessly to upload and execute the plan.
Drone Safety and Regulations: How To Operate A Drone
Safe and responsible drone operation requires understanding potential hazards and adhering to relevant regulations. This section addresses safety measures and legal compliance.
Potential Hazards and Safety Measures
Potential hazards include collisions with obstacles, loss of control, battery failure, and interference with other electronic devices. Safety measures include selecting appropriate flight locations, maintaining visual line of sight, avoiding crowded areas, and always having a backup plan.
Drone Regulations
Drone regulations vary by location. Always research and comply with local, national, and international laws concerning drone operation. These regulations often cover registration requirements, airspace restrictions, and operational limitations.
Common Drone Accidents and Prevention

| Accident | Cause | Prevention |
|---|---|---|
| Collision with obstacle | Loss of visual line of sight, poor piloting skills. | Maintain visual line of sight, practice safe piloting techniques. |
| Loss of control | Battery failure, interference, software glitches. | Use high-quality batteries, avoid interference sources, keep firmware updated. |
| Battery fire | Overcharging, damaged battery. | Use proper charging procedures, replace damaged batteries. |
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are crucial for keeping your drone in optimal condition. This section provides a maintenance schedule and guidance on resolving common problems.
Drone Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule ensures the drone’s longevity and reliable performance. This includes visual inspections, cleaning, and occasional component replacements.
- Weekly: Inspect propellers, clean the drone body, check battery health.
- Monthly: Inspect motor mounts, tighten screws, recalibrate sensors.
- Quarterly: Perform a more thorough inspection of all components, clean the camera lens.
Common Drone Malfunctions
- Low battery warning
- Loss of signal
- Motor failure
- GPS signal loss
- Gimbal malfunction
- Camera issues
Troubleshooting Common Drone Problems
Troubleshooting involves systematically checking components and settings to identify the root cause of a problem. Consult your drone’s manual for specific troubleshooting steps.
Drone Photography and Videography
Drones offer unique perspectives for photography and videography. Understanding camera settings and composition techniques is key to capturing high-quality aerial footage.
Camera Setting Adjustments

Adjusting aperture, shutter speed, and ISO affects image quality. Aperture controls depth of field, shutter speed affects motion blur, and ISO impacts image noise. Experiment with these settings to achieve your desired results.
Camera Angles and Shot Composition, How to operate a drone
Choosing appropriate camera angles and composition techniques significantly impacts the visual appeal of your aerial footage. Experiment with different angles, such as high-angle shots for wide landscapes or low-angle shots for dramatic perspectives.
Optimal Lighting Conditions
The best lighting conditions for aerial photography and videography typically involve soft, diffused light, avoiding harsh shadows and direct sunlight. The “golden hour” (sunrise and sunset) often provides beautiful, warm light. Avoid shooting directly into the sun, as this can cause lens flare and overexposure.
Successfully operating a drone is a rewarding experience that combines technical understanding with skillful piloting. From mastering basic controls to executing advanced maneuvers, this guide has equipped you with the knowledge to navigate the skies safely and responsibly. Remember to always prioritize safety, adhere to regulations, and continue practicing to refine your skills. The world awaits your aerial perspective!
Quick FAQs
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Understanding drone operation involves familiarizing yourself with its controls and safety protocols. A crucial step is learning about pre-flight checks and procedures, which are essential for safe and successful flights. For a comprehensive guide, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone to ensure you’re well-prepared before taking to the skies. Mastering these fundamentals will allow you to confidently and safely operate your drone.
Beginner-friendly drones often feature GPS stabilization and automated flight modes, simplifying operation and minimizing the risk of crashes. Look for models with clear instructions and user-friendly interfaces.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrating your drone’s compass before each flight is recommended, especially if you’re flying in areas with strong magnetic interference. This ensures accurate flight and prevents unexpected behavior.
What should I do if I lose signal with my drone?
Most drones have a “return-to-home” (RTH) function that automatically guides the drone back to its starting point if signal is lost. Familiarize yourself with this feature and practice its use in a safe environment.
How do I clean my drone’s propellers?
Gently clean your propellers with a soft brush and isopropyl alcohol to remove dirt and debris. Avoid harsh chemicals that could damage the plastic.
